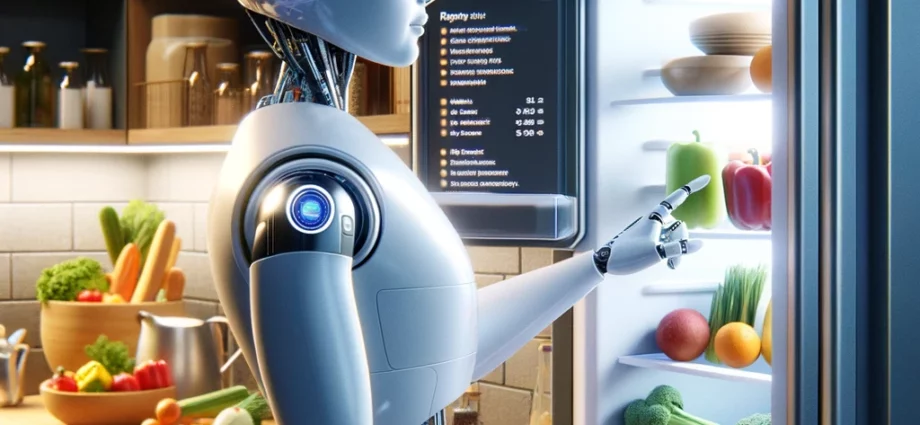
Roboticists are pushing the boundaries of technology by developing robots that can cook meals with the adaptability, common sense, and resourcefulness of a human chef, overcoming the limitations of traditional robotic programming.
Key Points:
- Ishika Singh and her team at the University of Southern California are working on creating robots capable of navigating a kitchen, selecting ingredients, and cooking meals tailored to specific cultures, kitchens, and dietary preferences.
- Classical robotics faces challenges with flexibility and adaptation due to predefined actions and environments, limiting robots to repetitive tasks in unchanging settings.
- Integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT with robotics aims to provide robots with a vast knowledge base and semantic understanding, potentially enabling them to perform complex tasks with human-like understanding and adaptability.
Detailed Summary:
In an era where robots can perform a myriad of tasks, from assembling cars to delivering packages, the quest for a kitchen-savvy robot represents a significant leap forward. Ishika Singh, a Ph.D. student at the University of Southern California, is at the forefront of this challenge, aiming to develop a robot that doesn’t just follow a recipe but can navigate the unique environment of a home kitchen, improvising meals based on available ingredients and specific dietary needs. This ambition highlights the limitations of classical robotics, which relies on a rigid planning pipeline, struggling to adapt to new and unforeseen situations.
The traditional approach to robotics, which requires programming every possible action and outcome, fails in dynamic environments like a home kitchen. Robots need to understand not just the mechanics of cooking but the nuances of taste, dietary restrictions, and even the mood of those they are cooking for. This complexity has stymied roboticists, making the adaptable dinner-preparing robot a “moonshot goal.” However, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT offers a glimmer of hope. These models, trained on vast amounts of text, provide the semantic understanding and flexibility that robots lack, suggesting a future where robots can access a wealth of human knowledge to inform their actions.
Despite the potential, integrating LLMs with robotics is not without challenges. Skeptics point to LLMs’ tendency to make errors, exhibit bias, or generate nonsensical responses. Nevertheless, successful examples of LLM-robot integration, like the prototype developed by Levatas and Boston Dynamics, demonstrate the potential for robots to understand and execute tasks based on natural language instructions. This breakthrough could redefine the role of robots in industrial settings and beyond, although replicating this success in the unpredictable environment of a home kitchen remains a formidable challenge. The journey toward a robot that can truly cook like a human is just beginning, blending the worlds of robotics, AI, and culinary arts in an exciting quest for innovation.
Source: Scientists Are Putting ChatGPT Brains Inside Robot Bodies. What Could Possibly Go Wrong?
Keep up to date on the latest AI news and tools by subscribing to our weekly newsletter, or following up on Twitter and Facebook.